
The most common cause of stratification is variation in the transporting ability of the depositing agent. No direct relationship exists between the thickness and extent of strata and the rate of deposition or the time represented for example, a stratum of limestone 2.5 cm (1 inch) thick may take longer to form than a stratum of sandstone 3 m (10 feet) in thickness.
#ROCK STRATA DEFINITION SERIES#
A sequence of strata, therefore, may appear as alternations of coarse and fine particles, as a series of colour changes resulting from differences in mineral composition, or merely as layers of similar aspect separated by distinct planes of parting. Stratification in sedimentary rocks may result from changes in texture or composition during deposition it also may result from pauses in deposition that allow the older deposits to undergo changes before additional sediments cover them. SpaceNext50 Britannica presents SpaceNext50, From the race to the Moon to space stewardship, we explore a wide range of subjects that feed our curiosity about space!ĭiamonds may be a girl’s best friend, but what is that mineral’s closest relative? Test your knowledge of rocks, minerals, and all things "yabba dabba doo" in this quiz.Learn about the major environmental problems facing our planet and what can be done about them!
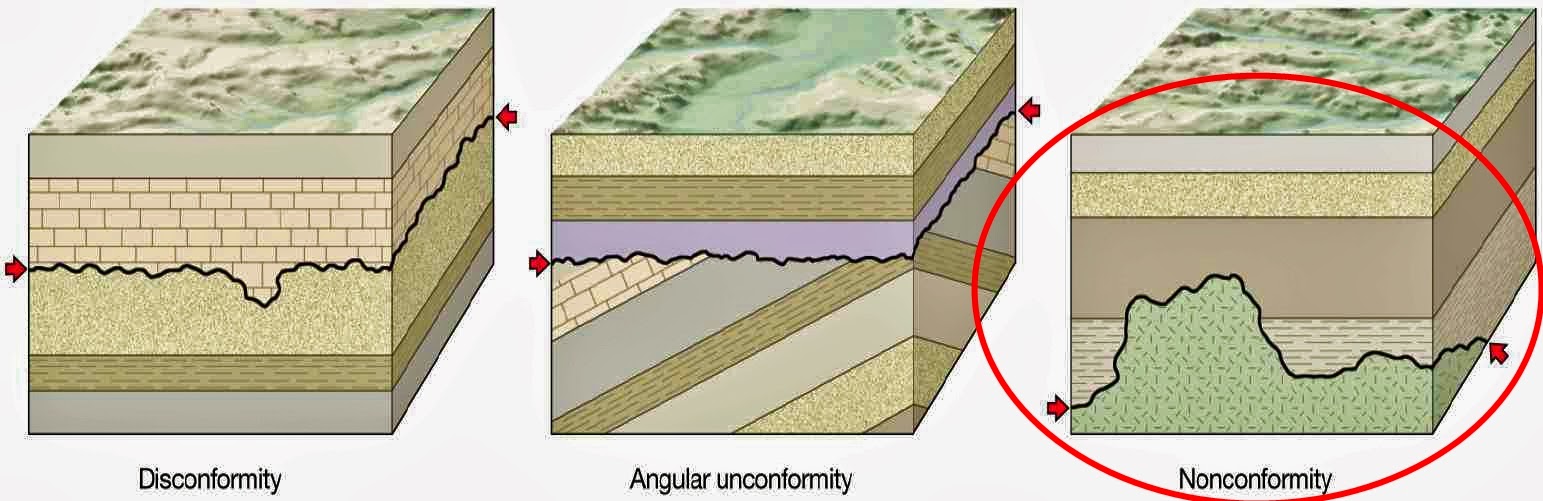
#ROCK STRATA DEFINITION HOW TO#

Large faults within the Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as subduction zones or transform faults. The fault surface can be vertical, horizontal, or at some angle to the surface of the earth. When an earthquake occurs on one of these faults, the rock on one side of the fault slips with respect to the other. A fault is a thin zone of crushed rock separating blocks of the earth's crust.

Fault means a mistake or a weakness.Īdditionally, what are the three types of fault? There are three different types of faults: Normal, Reverse, and Transcurrent (Strike-Slip). An example of fault is the San Andreas fault line in California. The definition of a fault is a weakness in the rock strata that can shift and create an earthquake. Thereof, what is a fault easy definition? Earth scientists use the angle of the fault with respect to the surface (known as the dip) and the direction of slip along the fault to classify faults. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
